기술동향
Finding an opening : A detailed structural analysis reveals new insights into the operating mechanism of a protein pore
- 등록일2009-04-14
- 조회수9626
- 분류기술동향
-
자료발간일
2009-03-10
-
출처
RIKEN Research
- 원문링크
-
키워드
#structural#protein pore#단백질
출처 : RIKEN Research
Finding an opening
A detailed structural analysis reveals new insights into the operating mechanism of a protein pore
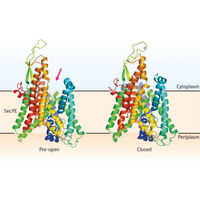
Figure 1: Model of the transition of the Sec translocon between the pre-open and closed forms. When SecA associates with SecYE, the complex rearranges into a ’pre-open’ state, which features an opening-indicated here by a pink arrow-through which proteins can be delivered. This opening is absent in the pore’s ’closed’ state
Many newly synthesized proteins will pass their lives within the confines of the cell, but many others end up secreted or embedded in the cellular membrane. Such proteins are labeled by specific ‘tags’ encoded in their sequences, which get recognized by proteins that escort them to the pore-like translocon protein complex. In bacteria, translocons are situated in the inner cell membrane. They remain effectively closed until they interact with an escorted protein, at which point the pore opens and allows the protein to pass through the membrane.
The central pore complex of the bacterial translocon is formed by a trio of proteins: SecY, SecE and SecG. Pore opening is initiated via interaction of the SecYEG complex with an additional protein, SecA, although many mechanistic details of this process remain unclear. Now, new work from a multi-institutional research team, led by Osamu Nureki of the University of Tokyo and Koreaki Ito of Kyoto University, and including RIKEN scientists Naoshi Dohmae and Yuji Sugita of the Advanced Science Institute in Wako, has yielded valuable new insights into this process1.
The team generated crystals of the SecYE complex from the bacterium Thermus thermophilus, assisted by the inclusion of an antibody fragment that helped to stabilize the complex, and then compared this structure against a previously determined structure of the ‘closed’ translocon from a primitive bacterial species that lacks SecA2. This comparison revealed the existence of an opening absent from the closed structure, suggesting that the SecYE-antibody complex had assumed a transitional ‘pre-open’ state.
Follow-up analysis yielded multiple lines of evidence that the antibody interaction with SecYE mirrors the association of this complex with SecA, suggesting that the structure seen here is a true intermediate in the translocon opening process, and that SecA binding induces formation of an entry point in SecYE for translocation-ready proteins. This transition of SecYE into the pre-open state also appears to induce major conformational s in SecA, which enable it to act as a motor for facilitating protein transit through the translocon pore.
Dohmae and Sugita are continuing to collaborate in the further examination of this mechanism, using chemical analysis techniques and computational simulations to confirm that the model developed based on these findings reflects the reality of how these proteins interact in the cell, but both researchers are pleased with these initial structural insights. “This crystal structure is useful to understand the early process of polypeptide translocation through Sec channels,” says Sugita.
Reference
1. Tsukazaki, T., Mori, H., Fukai, S., Ishitani, R., Mori, T., Dohmae, N., Perederina, A., Sugita,
Y., Vassylyev, D.G., Ito, K. & Nureki, O. Conformational transition of Sec machinery inferred
from bacterial SecYE structures. Nature 455, 988?991 (2008). | article |
2. Van den Berg, B., Clemons, W.M., Collinson, I., Modis, Y., Hartmann, E., Harrison, S.C. &
Rapoport, T.A. X-ray structure of a protein-conducting channel. Nature 427, 36?44 (2004).
The corresponding author for this highlight is based at the RIKEN Biomolecular
Characterization Team
...................(계속)
☞ 자세한 내용은 내용바로가기 또는 첨부파일을 이용하시기 바랍니다.
-
이전글
- 다기능 미세 단백질 사이모신 베타 4 (Thymosin β4)
-
다음글
- 만능 유도 줄기 세포 (induced Pluripotent Stem Cells, iPSCs)의 최신 연구 동향과 향후 전망
관련정보

