기술동향
The International Congress on Extremophiles '98에 다녀와서
- 등록일1998-03-01
- 조회수12896
- 분류기술동향 > 종합 > 종합
-
자료발간일
1998-03-01
-
출처
biozine
-
원문링크
-
키워드
#International Congress on Extremophiles#극한환경 미생물
한문희 박사 / 생명공학연구소 연구위원
1. ‘극한환경 미생물 국제 학술대회’의 개요
지난 1월 18일부터 22일까지 일본 Yokohama에서 열린 극한환경 미생물 국제 학술대회 (The International Congress on Extremophiles '98)에 패널 토론자로 초청되어 다녀왔다. 이번 대회에서는 학술발표가 끝난 후, `극 한환경 미생물의 미래(Future of Extremophiles)’ 라는 주제로 토론회를 갖고 앞으로 극한환경 미생물에 대한 과학기술 적 발전 방향 및 국제 협력 방안에 대해서 논의하였다. 이번 대회는 일본 해양과학기술센터(Japan Marine Science & Technology Center, JAMSTEC)의 DEEPSTAR(심해저 미생물 연구) 프로젝트 책임자로 있는 Koki Horikoshi 교수가 조 직위원장으로 대회를 주관했다. 극한환경 미생물에 관한 국 제학술대회는 유럽 EU 국가들과 일본이 주축이 되어 조직 되었다. 제1회 대회는 '96년에 포 르투갈에서 개최됐으며, 이번 대회는 두 번째가 된다. 다음 제3차 대회는 2000년에 독일 Hamburg에 서, 제4차 대회는 이태리에서 개최할 예정으로 있다.
이번 Yokohama 대회에는 세계 33개국에서 약 400여명의 이 분야 과학자들이 참여해서 그 간 연구해 온 극한환경 미생물에 관한 연구성과의 발표와 토의를 가졌다. 우리 나라에서는 연세대의 변유량 교수, 김유삼 교수와 건국 대 정선호 교수가 참석했으며, 생명공학연구소의 성문희 박사, 박진서 박사, KIST의 한예선 박사, 김선용박사, 해양연구소 김상진 박사 등 10 여명이 참 여했다. 개회 첫날에는 미국 Woods Hole 해양연구소의 Hogler W. Jannasch 박사 가 'The Deep-Sea's Contribution to the Extremophiles’라는 주제로 특강을 했다. 3일에 걸친 연구발표 대회는 1) genomics and molecular biology, 2) structure and function of biology, 3) physiology and metabolisms, 4) ecology and diversity 및 5) genome에 관한 주제로 나누어 40편의 초청연제 발표와 161편의 포스 터 발표가 있었다. 이중 우리 나라에서 는 성문희 박사 연구실에서 thermostable glutamate racemase에 관한 연구 를 박진서 박사 가 발표했으며, 7편의 포스터 발표를 해서 우리 나라에서도 극한환경 미생물에 관한 연구가 비록 그 규모는 적지만 조금씩 성과를 거두고 있음을 잘 보여주었다.
이번에 개최된 '극한환경 미생물의 미래'에 관한 토론회에서는 Horikoshi 교수를 비롯해 서 A. Aguilar Romanillos박사(Head of Unit, Demonstration Project, European Commission), I. Dundas교수(University of Bergen, Norway), J. P. Mckinley박사(Senior Research Scientists, Interfacial Geochemistry Group, Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, USA), A. A. Yayanos교수(University of California San Diego, USA), H. Horida박사(Executive Director, Deep-sea Research Department, JAMSTAC), 그리고 한국 에서는 본인이 참여했다.
European Commission의 Aguilar 박사는 European Commission의 생명공학 연구개발 사 업의 일환으로 시작된 극한환경 미생물 연구개발 사업에 대한 설명을 해 주었으며, 노르웨 이의 Dundas 교수는 심해저 의 극한 미생물에 관한 연구는 생명의 기원을 규명하는데 중요 한 역할을 할 것을 강조했다. JAMSTAC의 심해저 연구본부장인 Horida 박사는 JAMSTAC 의 심해저 연구의 중요성과 방향에 대해서 설명을 해 주었으며, McKinley 교수는 심해저의 지질학적 특성 과 미생물 생태에 관한 연구의 중요성에 대한 연구방향에 대해서 토의했다. 이어서, Yayanos 교수는 심해저 연구에 있어서 심해저 환 경요인, 소요장비 및 심해 미생물 의 연구대상 등에 관한 여러 가지 고려해야 할 요소들에 대해 설명을 했다. 본인은 주로 앞 으로 생명 공학 연구의 새로운 장을 열어줄 극한환경 미생물 탐색과 응용기술개발의 중요성 을 설명했다. 끝으로, Horikoshi 교수는 극한환경 미생 물의 연구방향을 1) 외계생물의 탐색, 2) 생명의 기원에 관한 연구와 같은 기초연구와 궁극적으로는 3) 이들 미생물을 이용한 산 업적 이용에 관한 기술개발의 중요성을 종합적으로 정리해서 결론을 내렸다 (그림 1).
2. 일본과 EC의 극한환경 미생물에 관한 연구개발 활동
이번 국제 학술대회에서 보듯이, 극한환경 미생물에 관한 기초연구 및 산업적 응용연구는 EC와 일본이 주축이 되어 적극 추진하고 있는 것을 알 수 있다. 이러한 맥락에서, 이들 국 가들이 주력하고 있는 극한환경 미생물 연구개발 사업의 주요 내용을 살펴보고자 한다.
일본의 극한환경 미생물에 관한 연구는 주로 JAMSTEC의 DEEPSTAR project로 적극 추진되고 있다. JAMSTAC은 과기청 산하 연구기관으로 1) 미지의 바다 탐색을 위한 심해 역 연구, 2) 지구환경변화를 해명하기 위 한 해양역의 연구, 및 3) 연해안의 미래 이용을 위 한 해역공간의 유효이용에 관한 해양 연구개발에 집중투자를 하고있다. 특히 심해저 연 구분 야에서 잠수탐사선 및 무인탐사기 등 여러 종의 심해저 탐사장비를 개발하여 심해저의 환 경, 지질 및 극한생물에 관한 연구를 여러 분야 의 전문가들이 종합적으로 공동 연구개발하 고 있다.

Horikoshi 교수가 주관하는 극한환경 미생물에 관한 연구는 심해저의 열수 또는 냉수가 분출 또는 용 출하는 해역의 특수환경 하에서 생존하고 있는 미생물을 대상으로 이들의 내 압, 내열, 내냉 기작 그리고 특수 단백질 등 생체물질의 특성을 구명하려는 목적으로 기초연 구를 추진하고 있다. 또한, 심해 미생물 연구를 효율적으로 지원하기 위해서 심해 미생물의 실험시스 템 개발과 계통보전에 관한 연구지원 사업도 아울러 추진하고 있다. 이 중, 심해저 미생물 실험시스템은 심해 미생물이 분포해 있는 심해저 의 泥土층을 잠수조사선 등으로 채 취해서 육상으로 운반한 후, 海中 미생물을 분리, 배양하는 일연의 조작과정을 심해의 압력, 온도조건 을 유지시킨 채로 시험할 수 있는 장치를 세계 최초로 개발해 냈음을 자랑하고 있 다. 이러한 시스템으로는 채니기, 희석장치, 분리장치 및 내압배양기 등 4개의 세부 시스템 으로 구성돼 있다. 또한, 심해 미생물의 계통보전을 위해서, 일본 내의 미생물 계통보전기관 과 협력해 서 연구결과로 얻어진 심해 미생물을 계통적으로 분류 보전해서 필요에 따라 제공 하는 체제를 정비하고 있다.
European Commission에서 하고 있는 극한환경 미생물의 연구개발 사업은 일찍이 1982년 에 European Union의 첫 번째 생명공학 프로그램으로 시작됐다. 이 프로젝트는 '96년에 와 서 `Extremophiles as Cell Factories’라는 기치 아래 종합연구개발 사업으로 확대 지원하 기 시작했다. 이 프로젝트에는 13개의 유럽 기업을 포함 해서 59개 연구기관이 참여하고 있 다. 이 프로젝트의 주요 목표는 극한환경 미생물의 극한 환경에서의 생존과 생산성 유지 기 작을 연 구하고, 유럽의 기업들로 하여금 이러한 극한환경 미생물을 탐구하여 세포공정에 응 용하도록 지원하는데 두고 있다. 이러한 극한 미생 물 프로젝트는 극한 미생물과 사업적 제 품의 탐색연구를 산·학협동으로 추진하는데 그 목적을 두고 있다. 탐색 연구대상으로는 내 열, 내 한, 내산, 내알카리, 및 내염성 미생물 등이 있으며, 연구대상 물질로는 효소와 단백질 (예, hydrolase, DNA-modifying enzymes 및 chaperonines) 그리고 새로운 생화학 물질(예, compatible solutes 및 lipids) 등에 주안을 두고 있다. 또한, 생명공 학적 연구개발의 주요과 제로는 1) genetic engineering, 2) product engineering(효소 & 단백질), 3) product engineering(생화학 물질), 4) bioreactor 및 fermentation process 등에 관한 주제분야에 초 점을 맞추고 있다.
3. 생명공학 발전에 있어서 극한환경 미생물 연구의 중요성
극한환경 미생물(extremophiles)이란 일반 미생물의 생존할 수 없는 극한환경 조건에서도 생존할 수 있 는 미생물을 통칭하며, 표 1에 요약한 바와 같이 온도, 압력과 같은 물리적 조 건 그리고 수소이온 농도, 염도, 습도, 용매, 금속이온 농도, 산소의 농도 그리고 탄수화물 이외의 영양물질 등 여러 가지 화학적 환경 조건에서 생존하는 미생물을 들 수 있다. 고압, 고온 및 황화수소의 존재 등 극한 환경이 가장 복합적으로 조성돼 있는 심해저 분출구 주변 의 침적토에서도 생존하는 고대 미생 물(Archeobacteria)이 발견됐으며, 인공배양까지 성공하 기에 이르렀다. 이러한 극한 미생물에 관한 탐구는 이제까지 우리가 상상도 못했던 환경조 건에서도 생물이 살고 있다는 사실을 입증해 냈을 뿐 만 아니라 생명의 기원을 구명하는 중 요한 자료로 그 값을 더해 주고 있다. 또한, 이러한 극한환경 미생물의 기초연구는 앞으로 생명공학 기술개발 과정에서 걸려있는 공정 상의 문제점을 보완 해결해 줄 수 있는 관건이 될 것이며, 생명공학의 실용적 응용영역을 넓혀 줄 계기가 될 것으로 확신한다.
일찍이, 극한환경 미생물의 응용은 발효식품에서 우리 조상들이 이용해 왔다고 할 수 있 다. 전통적 으로 장류 또는 젓갈류의 제조과정은 고염도에서 자라는 내염성 미생물 또는 효 소의 작용을 이용해 온 좋은 사례가 된다. 내온성 미생물 또 는 효소의 이용으로는 포도당 생성공정에서 사용되는 고온성 α-amylase, 이성화당을 만드는 glucose isomerase, PCR 과 정에 이용되는 내열성 DNA-polymerase 등이 있다. Alkalophile에 관한 연구는 Horikoshi 교수가 이 분야의 개척자로서 alkalophilic Bacillus 를 이용한 cyclodextrin의 생산, 세제용 알 카리성 protease 등의 개발은 좋은 사례가 된다.
앞으로, 생물공정을 공업적으로 또는 야외에서 실용화하는데 있어서 제약조건이 되는 여 러 가지 문 제를 해당되는 극한 조건에서도 생존하는 미생물의 탐색, 이들 미생물 또는 효소 의 활성기작 및 관련 유전자에 관한 연구를 통하여 좀더 현실적 으로 해결해 나갈 수 있을 것으로 기대된다. Thermophile 들은 생물공정을 고온 처리해서 보통 미생물의 오염을 방지 하고 반응속도를 촉 진시킬 수 있으며, halophile 들은 염분을 많이 쓴 식품공정이나 해양오 염 처리에 응용될 수 있다. Psychrophile은 보온이 안되는 야외에서 오염물질 처리공정에 잘 이용될 수 있으며, 유기용매 속에서 활성을 갖거나 안정한 미생물 또는 효소는 화학물질 전환 공정 에 유용하게 쓰일 수 있다. 탄수화물이 아닌 특수 유기 또는 무기물을 자화하는 미생물은 나날이 오염돼 가는 환경을 복원하는 공정에 이용될 수 있다.
이러한 극한환경 미생물에 관한 연구개발은 아직 초기 단계에 있기는 하나, 앞으로 이들 미생물의 탐 색과 응용연구는 새로운 생리활성 물질의 개발, 새로운 생물전환 공정 및 환경 복원기술 개발에 획기적인 길을 열어 줄 것이다. 이러한 극한환경 미생물의 탐색과 이들 미 생물에서 생성되는 효소, 단백질 또는 유전자의 기초연구와 더불어 유전공학, 단백질공학, 효소공학 내 지는 생물공정의 상호 연계연구는 생명공학의 실용성을 더 넓혀줄 것으로 확신 한다.
국내에서도 이러한 극한 미생물에 관한 연구는 `Biotech 2000’ 프로그램의 일환으로 시 작됐으나, 그 지원규모는 아직 작은 실정이다. 앞으로, 생명공학기술의 획기적 발전을 위해 극한 미생물에 관한 집중적 연구개발이 요구되 며, 이 분야의 전문가의 양성도 시급한 실정 이다.
아래에 기재된 `A new horizon opened for biotechnology with exploration of extremophiles’의 주제는 Yokohama 국제회의의 패날 토론회에서 발표한 내용으로 그 전 문을 소개하고자 한다.
A NEW HORIZON OPENED FOR BIOTECHNOLOGY WITH EXPLORATION OF EXTREMOPHILES
Moon Hi Han
Senior Research Fellow, KRIBB
I. Introduction
Biotechnology is a rapidly growing inter-disciplinary technological field utilizing the power of living cells or biodiversity to obtain goods and services for human needs. In particular, the use of microbial diversity for industrial processes and production of goods has long been practiced by men ever since they learnt how to make fermented foods and drinks. Historically, as shown in Fig. 1, the industrial application of microbial technology has been continuously advanced merging into modern biotechnology as knowledges in life sciences progressed. The microbial technology has been greatly progressed by technological innovations from natural mixed culture to pure culture systems and from surface culture to submerged culture systems. Such technological innovation has brought about extrinsic socio-economic impacts in its application in response to the needs of mankind.
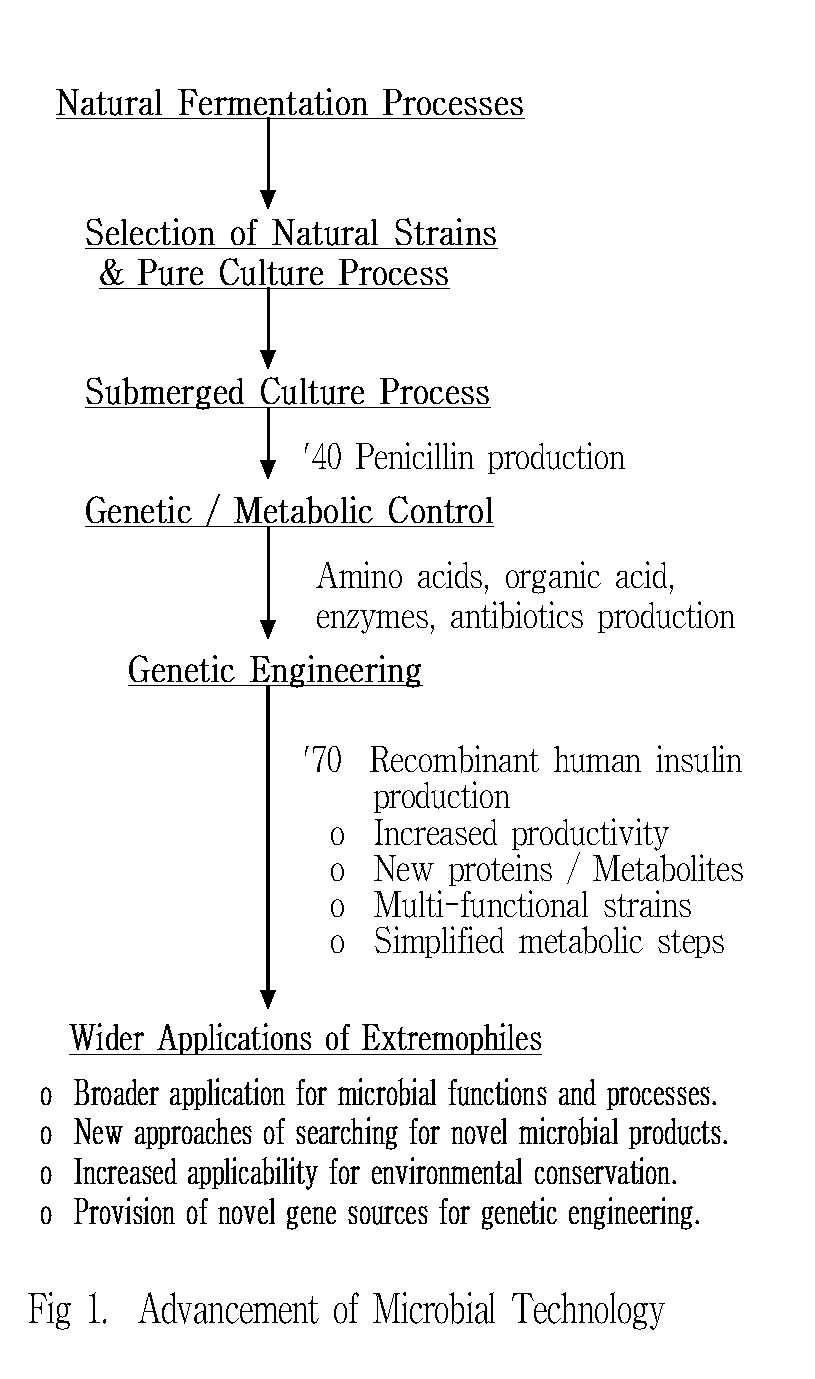
The most recent technological innovation has come with the development of genetic engineering technology in 1970's, based on scientific achievements in molecular biology. It has been well demonstrated that genetic engineering is a useful tool for making biotechnology more applicable in the development of bio-products and bio-processes. Recombinant DNA technology has made it possible for foreign gene products to be produced in different host cells, which do not originally the genetic code for production of the particular product.
However, it should be realized that there is a limit to gene technology since genetic information is limited to existing gene pools in the nature. Thus, exploitation and conservation of novel genetic resources will become increasing important tasks for the future expansion of application capacities of living cells. It appears that extremophiles, being among the least explored biological resources, has the highest potential for increased practical applicability of biotechnology. This will set a new road for technological innovation and open a new era for biotechnology in the 21st century.
I believe strongly that the exploration of extremophiles as new genetic and catalytic resources will make biotechnology more applicable and more practical for industrial processes and environmental conservation. In this regard, this International Congress on Extremophiles has particular significance for biotechnologists and microbiologists. The Congress will allow them to set new milestones for the future advancement of biotechnology.
II. Extremophiles that Open a New Era for Biotechnology
Biotechnology is based on the biochemical processes of living cells catalyzed by enzymes. Such biological processes have unique properties which have advantages over chemical processes. These properties are characterized by 1) high specificity with less by-product formation, 2) high efficiencies requiring a small amount of catalysts, and 3) environmental compatibility. They also utilize renewable resources as raw materials and can perform most chemical reactions through cellular metabolic pathways.
On the contrary, however, there is also intrinsic problem of limits of biological processes, either with living cells or isolated enzymes as shown in Table 1. These are 1) limited availability, 2) low stability of enzymes and cells, and 3) enzyme reaction systems restricted only to aqueous solutions. There are also limitations in operational conditions which require precise control of pH and temperature. It is for sure that research in biotechnology is aimed at solving these problems to broaden the industrial applicability of biological processes. To achieve the aims, there are two different approaches; i.e. 1) engineering of living cells or bio-processes and 2) exploration of new organisms with new biological functions such as extremophiles as summarized in Table 2.
|
| ||
| Problems | Microbial Cells | Enzymes |
|
| ||
| * Availability | Limited | Limited |
| * Metabolic Processes | By-product formation | No problem |
| * Solvent Systems | Restricted to aqueous solution | Restricted to aqueous solution |
| * Stability | Unstable | Unstable |
| * Co-factor regeneration | No problem | Limited |
| * Operational conditions | Limited | Limited |
|
| ||
The first approach is to increase efficiency of biological processes by manipulating cells genetically programed or by optimizing production processes. Currently, technological innovation comes through providing various scientific tools and means to manipulate genes, proteins, enzymes, and metabolic pathways for improvement of the productivity of cells. Genetic engineering, for example, provides technological tools for scientists to manipulate genes to create new forms of life and to increase productivity of pre-existing living organism. Unfortunately, however, modern technology has not reached a point as yet where it is capable of producing new genetic information other than that from already existing genetic resources.
Exploration of microbial diversity under extreme environmental conditions is an alternative approach to broaden the applicability of biological processes by the provision of novel genetic resources capable of solving the limits of biotechnology. As this congress has demonstrated, one can expect new and wide opportunities to open with the exploration of novel extremophiles, while some have been already proven to be useful for their industrial applications. The latter can be exemplified by thermophiles, acidophiles, and alkalophiles. Professor Horikoshi has already taken the initiative in research of alkalophiles and proven their practical application in industry.
| Problems | Ways of Solution | |
|
- Genetic engineering | - With novel catalytic systems |
|
- Metabolic engineering | - NA |
|
- Enzyme engineering | - Active in non-aqueous solvent systems |
|
- Enzyme engineering - Protein engineering |
- Stable under desired reaction conditions |
|
- Enzyme engineering - Use of whole cells |
- Not limited |
|
- Automated control - Continued processes |
- Active under desired operational conditions. |
Various extremophiles living under high pressure conditions, at low temperature, in the presence of organic solvents and heavy metals, and by utilizing different energy sources other than carbohydrates will give us a new dimension for improving currently available bio-processes and for screening new leading compounds. The application of such novel microbial diversity will also be a promising approach in attaining breakthroughs for bio-remmediation processes able to clean up the polluted environment in the future. We now know that environmental pollution is caused by toxic pollutants or over-nutritions which generate extreme conditions for ordinary microorganisms and eventually makes them incapable of recycling pollutants and clean-up the environment.
III. Needs to Explore Microbial Diversity for Sustainable Use
The exploration of microbial diversity including extremophiles should be carried out in reference to conservation and sustainable use as proclaimed by the Convention of Biodiversity. Today, there is a severe loss of biodiversity at an unprecedented rate caused by the over-exploitation of lands and oceans and by pollution caused by industrial development. Although there are some differences in estimated values among different reports, at least 20-55% of the world's biodiversity is predicted to disappear by the 21st century. It is also a concern that about 100 species are being rendered extinct by human activities every day. Currently, this has become a serious global concern.
Another current problem regarding biodiversity is that sometimes resources are over-extracted when the unexpected value of their products is exploited. Moreover, biodiversity is considered common property for all mankind and there is no well-defined concept of property rights for bioresources, which is rather strictly and clearly defined for the abiotic resources. At present, there is no available methodology for evaluating true values of genetic resources nor enough knowledges for understanding complete roles of microbial diversity in natural ecosystems.
At present, about 1.5-1.7 million species are identified and about 10 million species are estimated to live in the biosphere. The number of microbial species identified, for example, is about 13% (143 thousand species) out of total 1.12 million species estimated to exist on earth (Table 3). Most of microbial diversity has remained unexplored and has become extinct without knowing its value. The current loss of biodiversity including microbial diversity is not simply a matter of the reduced number of biological species in the global biosphere, but it is a matter of irreversible s in the human habitat and the catastrophic loss of goods and services, in particular precious genetic resources provided by the nature. I believe that extremophiles will be no exception in this crisis of extinction.
|
| |||
| Group | Known Species | World Species | Prodortion of Species Known |
|
| |||
| Algae | 40,000 | 60,000 | 67% |
| Bacteria(including Cyanobacteria) | 3,000 | 30,000 | 10% |
| Fungi(including Lichen-forming and yeasts) | 64,200 | 800,000 | 8% |
| Viruses(including plasmids and phages) | 5,000 | 130,000 | 4% |
| Protocists(including protozoa,excluding algae and fungal protocists) | 30,000 | 100,000 | 31% |
|
| |||
| Totals | 143,000 | 1,120,000 | 13% |
|
| |||
|
Source : Otto T. Solbrig, Biodiversity - Scientific Issues and Collaborative Research Proposals, 1991. |
It is known that genetic resources are indispensable for the development of genetic engineering and biotechnology. It is only in recent years the value of the variety of biological species and the vast pool of genes in nature has been recognized as vital for the future understanding their roles in the maintenance of balanced ecosystems. Genetic information does not merely mean the sequence of DNA, the carrier of genes, but the software resources provided and characterized by different structure and function of diverse biological species.
The development of biotechnology has allowed us to extract value from gene pools provided by the variety of biological species. Although current scientific knowledge and technology are not advanced enough to extract immediately economic value from diverse genetic resources, it does not mean that the resources are not useful for the future human needs. We must be aware that the extinction of biodiversity will directly lead to the loss of not only genetic information, the biological software programs essential for the existence of the global biosphere, but also useful resources for the advancement of biotechnology in the future. It means that exploration of extremophiles will have a dual significance for the provision of biotechnological tools and for understanding their roles in the ecological diversity.
IV. Epilogue
In conclusion, I would like to stress that biotechnological innovation will come through two ways, genetic manipulation of cell functions and exploration of new genetic resources, such as extremophiles. In history, microbial diversity has been a major bio-resource for the advancement of biotechnology. It will certainly continue to contribute to the future development of biotechnology. I believe that extremophiles are the last treasure of bio-resources provided by the nature for us.
They should be explored for the benefit of mankind, but it must be done in a sustainable manner. The research support for extremophiles should be expanded for the continued advancement of this newly emerging technological field. International and inter-disciplinary cooperation should also be promoted to facilitate building-up and sharing the frontier knowledge in this important scientific discipline.
-
이전글
- 노화과정에서 활성산소의 역할
-
다음글
- 최신연구도서

