기술동향
[신영숙] KRAS inhibitor 개발 동향
- 등록일2020-08-20
- 조회수8461
- 분류기술동향
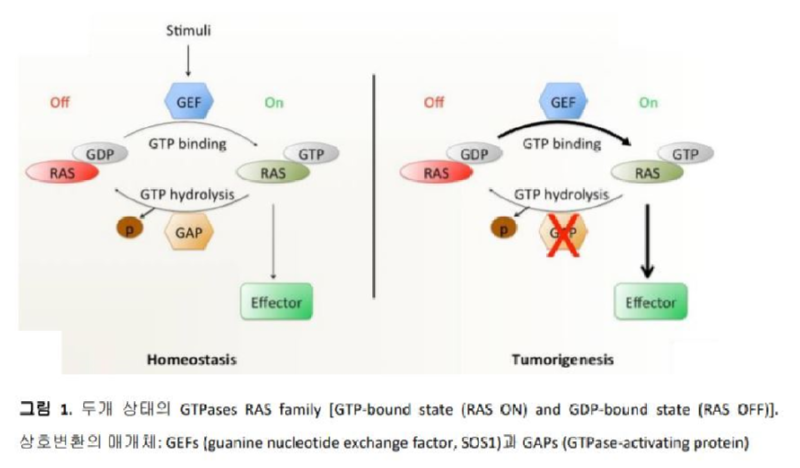
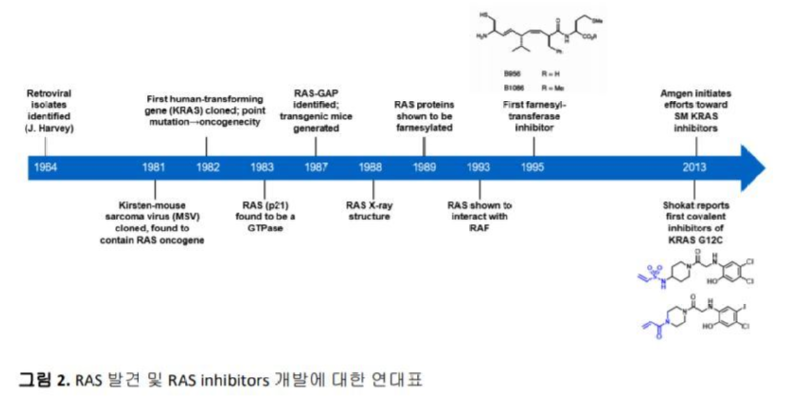
RAS의 발견과 RAS inhibitors의 개발을 연대기로 살펴보면 그림 2 와 같이 요약할 수 있다.6 RAS 에 관한연구는 1964년 Jennifer Harvey 가 leukemic rat으로부터 retrovirus 를 발견하면서부터 시작되었고, 이후에 RAS 종양유전자를 가진 세개의 retroviruses가 추가로 발견되었다. 1988년에는 RAS protein 의 X-ray crystal structure가 처음으로 발표되었고, RAS protein 이 farnesylation (prenylation) 되어야 암세포의 분화, 증식 및 생존이 가능해 진다는 보고에 기인하여 farnesyltransferase inhibitors (FTIs)를 개발하려는 여러가지 노력들이 시도 되었으나 임상시험에서는 다소 실망스러운 결과를 보여주었다.7 ATP는 protein kinases 에 대해 micromolar affinity를 가지기 때문에 다양한 ATP-competitive inhibitors의 개발이 가능하였으나, GTP는 RAS proteins에 대해 picomolar affinity를 가지므로 인해 GTP를 대체할 수 있는 GTP-competitive RAS inhibitors의 개발은 그리 쉽지 않았다. 이외에도 여러가지 방법으로 RAS와 관련된 항암제의 개발에 관한 연구가 수십년간 시도되어 왔으나 임상으로까지 이어진 항암제는 없었기에 RAS는 “undruggable”한 타겟으로 간주되어 왔다. 2013년에 University of California, San Francisco의 Kevan Shokat 교수와 그의 연구진들이 KRASG12C protein의 Switch II 근처에 있는 G12C의 cysteine과 covalent inhibitor가 결합하며 생긴 새로운 pocket을 발견하였는데, 이 pocket은 apo crystal structures에서는 발견되지 않고 KRASG12C protein이 inactive GDP-bound form으로 존재할 때만 만들어지는 매우 얕은 allosteric binding pocket이었다. 이 pocket의 발견은 새로운 접근 방법으로 KRAS inhibitor의 개발을 가능하게 만든 매우 의미 있는 발견이었다.8
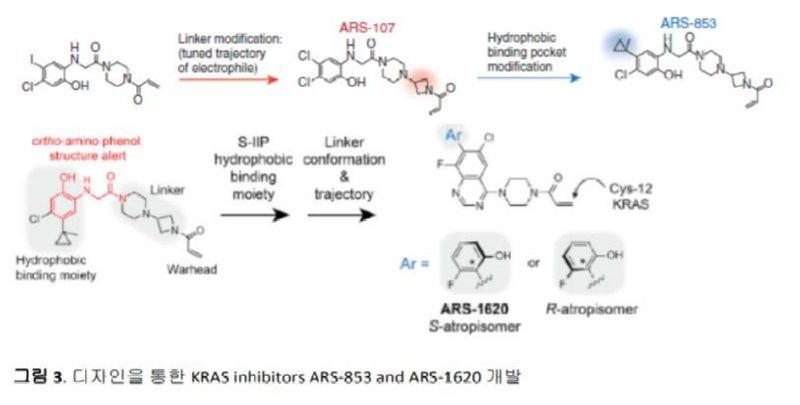
2016년에는 Shokat 교수에 의해 설립된 Araxes Pharma의 자회사인 Wellspring Biosciences에서 이보다 더 개선된 물질인 ARS-853을 개발하였으나 ARS-853은 동물실험에 사용될 수 있는 정도의 효능은 보이지 못하였다.9 그들은 ARS-853의 지속적인 구조-효능-관계 (Structure-Activity-Relationship, SAR) 최적화 과정을 통하여 ARS-1620를 개발하였고, ARS-1620는 동물실험에서 tumor regression을 보여 주는데 성공하였다 (그림 3).10
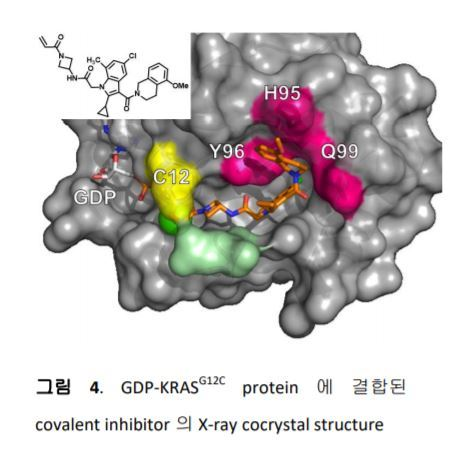
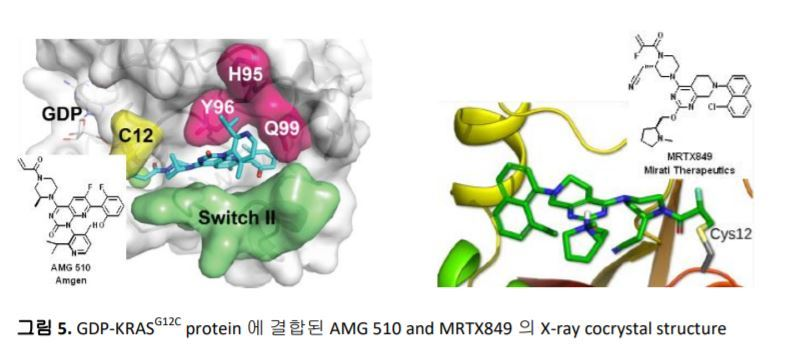
Amgen은 Carmot와의 공동연구를 통하여 Switch II 근처에 특정구조를 가진 covalent inhibitor가 G12C 와 결합하면서 만들어지는 새로운 ‘cryptic pocket’을 발견하였고, 그 새로운surface area를 통해 inhibitors의 RAS protein 에 대한 binding affinity를 증가 시킬 수 있었다 (그림 4).12 이 화합물을 시작으로 SAR분석을 통한 최적화 과정을 통하여 더욱 개선된 효능과 pharmaceutical properties를 갖는 AMG 510을 개발하여 2018년 8월에 first-in-class로 KARSG12C inhibitor의 임상시험을 시작하였다 (그림 5).13, 14
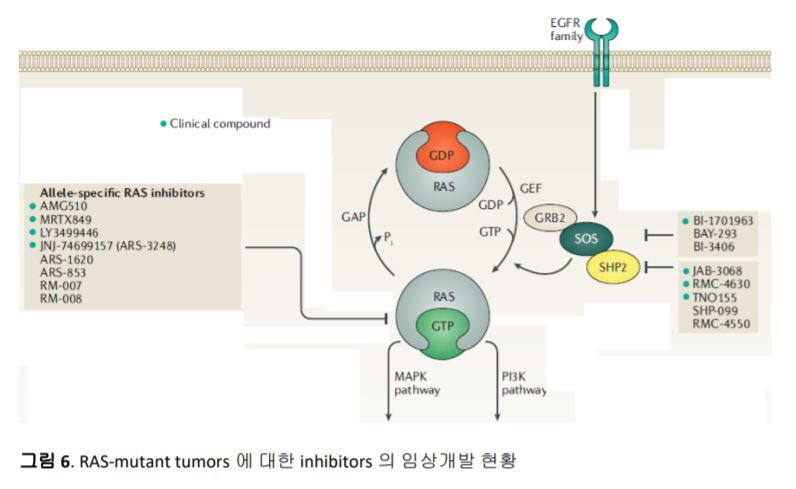
RAS mutations을 직간접적으로 타겟하는 방법으로 현재 임상시험 중이거나 preclinical 단계에 있는 연구들은 그림 6에 요약되어 있다.16 Revolution Medicines은 GTP-bound state (RAS ON)을 타겟으로 하는 tri-complex inhibitor RM-007과 RM-008의 개발을 진행하고 있다. Boehringer Ingelheim은 SOS1-mediated nucleotide exchange를 저해하기 위하여 KRAS-SOS1 binding을 막는 SOS1 inhibitor BI-1701963을 개발하여 현재 임상1상 시험중이며, Bayer 역시 SOS1 inhibitor를 개발 중인 것으로 알려져 있다. SOS1 inhibitors는 KRASG12C inhibitors와는 달리 pan-KRAS inhibitors 로서 모든 KRAS mutations에 작용한다는 장점이 있다. 하지만 비임상 실험에서 SOS1 inhibitors이 단독요법으로 사용된 경우 partial tumor growth inhibition에 그쳐서 임상시험에서는 단독요법과 더불어 MEK inhibitor Trametinib과의 병용요법도 함께 진행중이다. Non-receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase로서 MAPK pathway에서 중요한 역할을 하고 있는 SHP2 inhibitors의 개발에 대한 시도도 이루어 지고 있다. 이미 Revolution Medicines는 RMC-4630을, Novartis는 TNO155를, 그리고 Jacobio Phamaceuticals은 JAB-3068을 개발하여 단일요법 혹은 병용요법으로 임상시험을 시작하였다.
이외에도 Moderna 와 Merck는 G12C, G12D, G13D, G12V mutations을 타겟으로 하는 cancer vaccine mRNA-5671을 가지고 임상시험을 시작하였다.
뿐만 아니라 요즘 많은 사람들이 관심을 가지고 있는 proteolysis targeting chimera (PROTAC) 기술을 이용한 항암제 개발도 시도되고 있으며, 최근에는 그 가능성을 보여준 연구 보고도 있었다.17, 18
이처럼 KRASG12C inhibitor AMG 510이 이미 임상시험에서 주목할 만한 결과를 보여주었고, 현재 다양한 방법으로 KRAS inhibitors의 개발이 이루어 지고 있으므로 KRASG12C mutated cancer뿐만 아니라 다른 KRAS mutated cancers 역시 더 이상 “undruggable”한 타겟으로 남겨지지 않게 될 것이라고 기대해 볼 수 있다.
2. Hobbs, G. A.; Der, C. J.; Rossman, K. L., RAS isoforms and mutations in cancer at a glance. J Cell Sci 2016, 129 (7), 1287-92.
3. Prior, I. A.; Lewis, P. D.; Mattos, C., A comprehensive survey of Ras mutations in cancer. Cancer Res 2012, 72 (10), 2457-67.
4. Haigis, K. M., KRAS Alleles: The Devil Is in the Detail. Trends Cancer 2017, 3 (10), 686-697.
5. Iris Z. Uras, H. P. M., Emilio Casanova, Targeting KRAS mutant NSCLC_past, present, and future. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4326.
6. Malumbres, M.; Barbacid, M., RAS oncogenes: the first 30 years. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3 (6), 459-465.
7. Cox, A. D.; Fesik, S. W.; Kimmelman, A. C.; Luo, J.; Der, C. J., Drugging the undruggable RAS: Mission Possible? Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 2014, 13 (11), 828-851.
8. Ostrem, J. M.; Peters, U.; Sos, M. L.; Wells, J. A.; Shokat, K. M., K-Ras(G12C) inhibitors allosterically control GTP affinity and effector interactions. Nature (London, U. K.) 2013, 503 (7477), 548-551.
9. Patricelli, M. P.; Janes, M. R.; Li, L.-S.; Hansen, R.; Peters, U.; Kessler, L. V.; Chen, Y.; Kucharski, J. M.; Feng, J.; Ely, T.; Chen, J. H.; Firdaus, S. J.; Babbar, A.; Ren, P.; Liu, Y., Selective Inhibition of Oncogenic KRAS Output with Small Molecules Targeting the Inactive State. Cancer Discovery 2016, 6 (3), 316-329.
10. Janes, M. R.; Zhang, J.; Li, L.-S.; Hansen, R.; Peters, U.; Guo, X.; Chen, Y.; Babbar, A.; Firdaus, S. J.; Darjania, L.; Feng, J.; Chen, J. H.; Li, S.; Li, S.; Long, Y. O.; Thach, C.; Liu, Y.; Zarieh, A.; Ely, T.; Kucharski, J. M.; Kessler, L. V.; Wu, T.; Yu, K.; Wang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Deng, X.; Zarrinkar, P. P.; Brehmer, D.; Dhanak, D.; Lorenzi, M. V.; Hu-Lowe, D.; Patricelli, M. P.; Ren, P.; Liu, Y., Targeting KRAS Mutant Cancers with a Covalent G12C-Specific Inhibitor. Cell (Cambridge, MA, U. S.) 2018, 172 (3), 578-589.e17.
11. Amgen, Amgen Announces New Clinical Data Evaluating Novel Investigational KRAS(G12C) Inhibitor in Larger Patient Group at WCLC 2019, https://www.amgen.com/media/news-releases/2019/09/amgen-announces-new-clinical-data-evaluating-novel-investigational-krasg12c-inhibitor-in-larger-patient-group-at-wclc-2019/. 2019.
12. Shin, Y.; Jeong, J. W.; Wurz, R. P.; Achanta, P.; Arvedson, T.; Bartberger, M. D.; Campuzano, I. D. G.; Fucini, R.; Hansen, S. K.; Ingersoll, J.; Iwig, J. S.; Lipford, J. R.; Ma, V.; Kopecky, D. J.; McCarter, J.; San Miguel, T.; Mohr, C.; Sabet, S.; Saiki, A. Y.; Sawayama, A.; Sethofer, S.; Tegley, C. M.; Volak, L. P.; Yang, K.; Lanman, B. A.; Erlanson, D. A.; Cee, V. J., Discovery of N-(1-Acryloylazetidin-3-yl)-2-(1H-indol-1-yl)acetamides as Covalent Inhibitors of KRASG12C. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10 (9), 1302-1308.
13. Lanman, B. A.; Allen, J. R.; Allen, J. G.; Amegadzie, A. K.; Ashton, K. S.; Booker, S. K.; Chen, J. J.; Chen, N.; Frohn, M. J.; Goodman, G.; Kopecky, D. J.; Liu, L.; Lopez, P.; Low, J. D.; Ma, V.; Minatti, A. E.; Nguyen, T. T.; Nishimura, N.; Pickrell, A. J.; Reed, A. B.; Shin, Y.; Siegmund, A. C.; Tamayo, N. A.; Tegley, C. M.; Walton, M. C.; Wang, H. L.; Wurz, R. P.; Xue, M.; Yang, K. C.; Achanta, P.; Bartberger, M. D.; Canon, J.; Hollis, L. S.; McCarter, J. D.; Mohr, C.; Rex, K.; Saiki, A. Y.; San Miguel, T.; Volak, L. P.; Wang, K. H.; Whittington, D. A.; Zech, S. G.; Lipford, J. R.; Cee, V. J., Discovery of a Covalent Inhibitor of KRAS(G12C) (AMG 510) for the Treatment of Solid Tumors. J Med Chem 2020, 63 (1), 52-65.
14. Canon, J.; Rex, K.; Saiki, A. Y.; Mohr, C.; Cooke, K.; Bagal, D.; Gaida, K.; Holt, T.; Knutson, C. G.; Koppada, N.; Lanman, B. A.; Werner, J.; Rapaport, A. S.; San Miguel, T.; Ortiz, R.; Osgood, T.; Sun, J.-R.; Zhu, X.; McCarter, J. D.; Volak, L. P.; Houk, B. E.; Fakih, M. G.; O’Neil, B. H.; Price, T. J.; Falchook, G. S.; Desai, J.; Kuo, J.; Govindan, R.; Hong, D. S.; Ouyang, W.; Henary, H.; Arvedson, T.; Cee, V. J.; Lipford, J. R., The clinical KRAS(G12C) inhibitor AMG 510 drives anti-tumour immunity. Nature (London, U. K.) 2019, 575 (7781), 217-223.
15. Fell, J. B.; Fischer, J. P.; Baer, B. R.; Blake, J. F.; Bouhana, K.; Briere, D. M.; Brown, K. D.; Burgess, L. E.; Burns, A. C.; Burkard, M. R.; Chiang, H.; Chicarelli, M. J.; Cook, A. W.; Gaudino, J. J.; Hallin, J.; Hanson, L.; Hartley, D. P.; Hicken, E. J.; Hingorani, G. P.; Hinklin, R. J.; Mejia, M. J.; Olson, P.; Otten, J. N.; Rhodes, S. P.; Rodriguez, M. E.; Savechenkov, P.; Smith, D. J.; Sudhakar, N.; Sullivan, F. X.; Tang, T. P.; Vigers, G. P.; Wollenberg, L.; Christensen, J. G.; Marx, M. A., Identification of the Clinical Development Candidate MRTX849, a Covalent KRAS(G12C) Inhibitor for the Treatment of Cancer. J Med Chem 2020, 63, 6679−6693.
16. Moore, A. R.; Rosenberg, S. C.; McCormick, F.; Malek, S., RAS-targeted therapies: is the undruggable drugged? Nat Rev Drug Discov 2020, Online ahead of print, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41573-020-0068-6.
17. Bond, M. J.; Chu, L.; Nalawansha, D. A.; Li, K.; Crews, C. M., Targeted Degradation of Oncogenic KRASG12C by VHL-Recruiting PROTACs. ACS Central Science 2020, Ahead of Print.
18. Wang, M.; Lu, J.; Wang, M.; Yang, C. Y.; Wang, S., Discovery of SHP2-D26 as a First, Potent, and Effective PROTAC Degrader of SHP2 Protein. J Med Chem 2020.
☞ 자세한 내용은 내용바로가기 또는 첨부파일을 이용하시기 바랍니다.
동향
- 기술동향 발암유전자 KRAS를 겨냥한 맞춤형 암 치료의 새로운 장 2025-05-21
- 기술동향 [Laura Soucek] Trends in the development of a clinically-viable Myc inhibitor 2020-04-14
- 기술동향 항암면역치료제 중 checkpoint inhibitor, 항체약물접합체, chimeric antigen receptor T-cell 연구 동향 2018-09-13
- 기술동향 Roaming receptors 2009-07-31
- 기술동향 A small molecule kinase inhibitor for CNS diseases: Dr. Larry Park 2005-05-13

